Hacker Perspective: Climate Science / Climate Change
CAVEAT: Many external links on this page stopped working in 2025 when the second Trump administration instructed NASA and NOAA to remove "climate material" from their websites. I am now in the process of updating the links to ABC (Australia, Britain, Canada) sources.
- Executive Summary
- General Summary
- Climate Warming concerns from Isaac Asimov PhD
- Three good 'climate science' sites for citizens and laypeople
- Shocking Revelations about American Climate Denial
- Climate Change 1: Global Warming food-for-thought
- Climate Change 2: It Is All About the Ice (polar as well as glacial)
- Climate Change 3: Global Dimming seems to play a roll
- Climate Change 4: Comparing Earth to Venus and Mercury
- Climate Change 5: Global Warming is an observational fact because...
- CO2 levels are rising while Oxygen levels are falling (yikes!)
- The annual rate-of-change of Sea-level rise has already doubled, and continues to increase
- Proof: The burning of fossil fuels is mostly to blame because there is too little carbon-14 in atmospheric CO2
- Climate Change 6 - Incontrovertible facts
- Climate Change 7 - Improving atmospheric CO2 extraction of trees (a temporary solution which is better than nothing)
- A chemical analysis of burning gasoline (petrol for you Brits) shows that:
burning one pound of gasoline produces three pounds of carbon dioxide
burning one Kg of gasoline produces three Kg of carbon dioxide - Is 'too much' CO2 good or bad?
- Reaping What We Sow - CO2 pushes plants to increase carbohydrates while reducing protein
- Cognitive Dissonance (or "How We Fool Ourselves")
- Politics and Anti-Science
- Art Imitates Life (some people worried about global warming in 1973)
- Ancient Information from 2009 (includes info about ExxonMobil promoting "their" scientific experts for the American delegation to the IPCC)
- Related Links
- Even though Venus is closer to the Sun, albedo causes Venus to receive 25% less
solar energy than Earth but the average surface temperature is 30 times higher on the Celsius scale (462 °C) and 14 times higher on the Fahrenheit scale
(864 °F). In fact, Venus is hotter than Mercury (200-330 °C) even though Mercury is much closer to the Sun. So why is Venus so hot?
Answer: Its atmosphere is composed of 95% CO2 which has caused a runaway greenhouse effect. Notice that the planet is doing just fine but is of zero value in supporting life. Click here
to see the details below.
- Meanwhile, here on Earth, atmospheric CO2 levels are rising while Oxygen levels are falling. If plant-life in the biosphere was
able to adapt to higher CO2 levels as many climate change deniers claim, then we would expect reduced (or zero) levels of change. Put another way: our
biosphere is losing the battle with human-produced changes starting with the industrial revolution. Click here to see the details
below.
- A secondary school chemical analysis proves that burning one pound of gasoline produces three pounds of carbon dioxide.
Click here to see the details below.
Comment: burning other fossil fuels, including natural gas, diesel or coal are not much different.
- On the one-hundredth anniversary of the oil industry in 1959, Edward Teller (the father of the hydrogen bomb) warned about the dangers associated with rising levels
of CO2
https://www.skepticalscience.com/hundredth-birthday-1959-teller-oil-global-warming.html
Fans of capitalism should ask themselves: why does an industry that began in 1859 still receive government subsidies?
Climate Warming concerns from Isaac Asimov (PhD Biochemistry)
Between 1940 and 1990 there existed a cadre of great American explainers who were able to inform the public about topics involving science. Examples include people like Isaac Asimov, Carl Sagan, and Richard Feynman to only name three of many. Since their deaths, I have noticed the public slowly shift from the pragma of science toward the dogmas of politics and religion. Meanwhile it would seem that intelligent conversation is on the decline.| Title | Mins | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Isaac Asimov (1977-05-21) www.youtube.com/watch?v=iz1g55H6XgA |
4:58 |
The Greenhouse Effect
|
| Isaac Asimov (1989-01-14) www.youtube.com/watch?v=LO0sCs8jI4k |
10:04 | Part 1 - The Threats to Humanity |
| Isaac Asimov (1989-01-14) www.youtube.com/watch?v=TpHPQCnHHl4 |
10:19 | Part 2 - The Answer for Humanity |

Isaac Asimov PhD (Biochemistry)
Author of fiction and non-fiction
CBC Radio Broadcast Date: May 21, 1977
What does the greenhouse effect have to do with a greenhouse? And how does it work? In this 1977 clip from the CBC Radio program Quirks and Quarks, popular science author Isaac Asimov tells us all about the greenhouse effect and how it could be warming up the Earth. He also explains why we should care. "This greenhouse effect can be very serious," says Asimov, "and it's something that we have to take into account."
https://www.cbc.ca/archives/entry/why-is-it-called-the-greenhouse-effect
Program Transcript| David Suzuki |
Isaac, we've been talking about a lot of words this year that most of our listeners may never have heard before. Do you have one that has become common in our everyday language? |
| Isaac Asimov |
Well, how about "Greenhouse Effect"? We know what a greenhouse is. It's a very common thing. Now, as you know, a greenhouse is made almost entirely of glass. And you figure, why glass? And the answer to that is that glass is transparent to visible light but not so transparent to infrared light. Infrared light is like visible light but has got longer waves. The longer the waves, the less energy it has. Now here's what happens; the high energy visible light from the sun goes through, and it heats up whatever is inside the greenhouse. Whatever is inside the greenhouse re-radiates energy but at a lower energy intensity. So, it doesn't re-radiate visible light, it re-radiates infrared. And that won't go through the glass very well, so the heat is trapped inside the glass. The sunshine comes down, gets inside, stays there so to speak, so that the temperature inside the greenhouse is always higher than it is outside. And you manage to keep the plants growing even when, outside, it would be too cold for them to grow. Well then, anything which has this effect of allowing visible light to pass and being a barrier to infrared is said to have "a greenhouse effect" |
| David Suzuki |
Um hmm |
| Isaac Asimov |
Now, one of the substances that has a greenhouse effect is carbon dioxide. Carbon dioxide is transparent to visible light, but it absorbs infrared; it acts as a heat shroud. Now in our atmosphere there are 3 hundredths of a percent of carbon dioxide. This isn't much but it is enough to trap some heat and make the surface of the Earth warmer by a little bit then would otherwise be. Now when we are burning fuel at all times, coal and oil, we are always pouring carbon dioxide into the air. Some of the carbon dioxide dissolves in the oceans, some of it reacts with certain chemicals in the soil, but there's enough that gets into the atmosphere so that it's going up slightly. And possibly by the time, um, say, another 50 years or so, it might, instead of 3 hundreds of a percent, it might be 5 hundreds of a percent. Well, we'll never know the difference; carbon dioxide isn't particularly bad for us in that small quantity, we'll just breathe. But it's going to stop enough extra heat so that the surface of the Earth might be just a degree, or so, warmer on the average than it is now. Well, this too, isn't too bad. We can manage. The summers will be a little warmer and the winters a little milder. But the peculiar thing is that perhaps this little additional heat on the Earth, generally, might suffice to start melting the ice caps. In other words, right now they melt a little in the summer, and they freeze a little in the winter, and there's a balance. But if the Earth gets even a little warmer, maybe a little more will melt in the summer and a little bit less will freeze in the winter, and little by little they'll start melting. And all that water will run into the ocean and raise the level 200 feet (~ 51 m) and drown all the coasts, so that this greenhouse effect can be very serious and is something we have to take into account as we're working along. Now the planet Venus has a thick atmosphere which is 95 percent carbon dioxide. It has a runaway greenhouse effect and the temperature on the planet Venus is something like 500 degrees Centigrade (932 F) [which is] hot enough to melt lead. Entirely because of the heat trap of the atmosphere. |
| David Suzuki |
That really worries me because my wife and I live right on the ocean, in the ah, Pacific Ocean. |
| Isaac Asimov |
Well, I need not say that New York is right on the Atlantic Ocean. |
| David Suzuki |
Right. What was the, ah, concern, a while back, with the SST; that it might increase the greenhouse effect. What was the argument there? Do you know? |
| Isaac Asimov |
Well, the SST would release... see, carbon dioxide isn't the only molecule, uh, that acts as a greenhouse effect, there are other complicated molecules that do so, also. Ah, nitrous oxide, methane, and so on. Uh, but they are present in the atmosphere is far smaller quantities. But the SST can release these molecules in the upper atmosphere, and uh, even small quantities can trap a little more heat. Also, they can react with the ozone layer... |
| David Suzuki |
Um hmm |
| Isaac Asimov |
...so that it also might threaten the ozone layer. This is not something which is absolutely certain, but some scientists thought we oughtn't to have taken chances like that either |
| David Suzuki |
Thanks a lot Isaac. |
page-121: Whatever the cause of the ice ages may have been, it seems now that man himself may be changing the climate in store for the future. The American physicist Gilbert N. Plass has suggested that we may be seeing the last of the ice ages, because the furnaces of civilization are loading the atmosphere with carbon dioxide. A hundred million chimneys are ceaselessly pouring carbon dioxide into the air; the total amount is about six billion tons a year 200 times the quantity coming from volcanoes. Plass pointed out that since 1900 the carbon dioxide content of our atmosphere has increased about 10 per cent. This addition to the earth’s “greenhouse” shield against the escape of heat, he calculated, should raise the average temperature by about 1.1 degrees C. per century. During the first half of the twentieth century the average temperature has indeed risen at this rate
A few good 'Climate Science' information sites for citizens
| Site name | URL |
|---|---|
| NASA Climate | https://climate.nasa.gov/ |
| Skeptical Science | http://www.skepticalscience.com (just the facts) |
| Science of Doom |
https://scienceofdoom.com |
| Peter Hadfield | https://www.youtube.com/user/potholer54 (great debunker of internet-generated nonsense) |
| This is not Cool | https://thinc.blog/ (was http://climatecrocks.com) |
It all begins in 1827 with the study of heat flow by Jean-Baptiste Joseph Fourier An introduction to climate change science for:
- school teachers
- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=i8Y9-XCLqiA - Professor Richard Wolfson (2016-05-11)
- citizens
- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=52KLGqDSAjo - Climate Change -- the scientific debate
- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=P70SlEqX7oY (1/2)
- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=eJFZ88EH6i4 (2/2)
- 2009 content moved here to reduce size
Shocking Revelations about American Climate Denial
Despite data being collected for over half a century, despite a President (Lyndon Johnson) being warned about the looming threat of a changing climate in the mid-1960s, and despite plants and animals now changing their behavior to fast-altering conditions, a few scientists continue to raise doubts regarding climate science and its findings. Naomi Oreskes sees a pattern. The pattern repeats itself in a string of issues including controversy over tobacco smoke, the dangers of acid rain, and DDT.UCSD (University of California at San Diego) Professor of History and Science Studies Naomi Oreskes Ph.D. presented this 58-minute lecture on the History of Global Warming Science titled The American Denial of Global Warming
- www.youtube.com/watch?v=2T4UF_Rmlio (video: 58-minute lecture)
- Many viewers will be surprised to learn that "the science of climate change" has been settled (more or less) for five decades
- Naomi Oreskes is also a co-author of the 2010 book Merchants of Doubt
39-second extract from the December-2014 movie MERCHANTS OF DOUBT https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=cpbZCPvCEjQ
quote: Asbestos, Global Warming, DDT, Acid Rain, Tobacco, Ozone. There is a bit of a mystery [as] to what all these things have in common. All these issues are issues that involve the need for government action. That's when the penny dropped {euphemism} because then I began to realize that none of this is about "the science". All of this is a political debate about the roll of government. So in a number of places, we actually found these people saying: they see environmentalists as creeping communists, they see them as reds under the bed, they call them watermelons; green on the outside and red on the inside. And they worry that environmental regulation will be a slippery slope to socialism.
NSR Comment: Just as a non-trivial fraction of 1950's North America willfully fell under the spell of McCarthyism, the same thing has been happening over the past 30 years with the environment. Carl Sagan was correct when he said, "Science is a way of thinking" so let me add this: "Politics is a way of not-thinking" and adding religion to the mix only makes things worse. I wonder how much permanent damage will occur before the majority wakes up from "this madness"
Question: Why Do Americans Continue to Deny Climate Change? Answer: ... well, I'm so glad that you emphasized that it is really only in the United States that this is happening. And it's not even happening in most of the Unites States [and parts of western Canada]. The deniers have a large megaphone, and it's called FOX NEWS and the rest of the right-wing media machine. But if you look at the numbers, really look at the numbers, it's just a minority of people who believe this [stuff]. Now. Why. It is a sizeable minority, so I don't mean to say it is not, so why in the United States and not elsewhere. I think there are two basic reasons. One. Is that the United States historically, and today, has had a much stronger fossil fuel industry than any other advanced industrial nation. Look at Europe. They don't have, and haven't had, historically, major oil companies. In Britain there was British Petroleum. That was their company. In the Netherlands, Royal Dutch Shell. But the big oil companies historically have been US based, and most of their money originally came from here, in the United States. Drilling in Texas, Oklahoma and here in California. And they became, the oil industry in particular, became the single richest business enterprise in human history. Let me emphasize that "the single richest business enterprise EVER". They know perfectly well that if we take climate science seriously that they will have to sell less product. And so, they have, as has been well reported and I talk a bit in the book, they've spent literally millions of dollars on a very calculated disinformation campaign for twenty years that has been torn out of the playbook by the tobacco industry. And in fact, used the very same scientist, [physicist] Fredrick Seitz [founding chairman of the George C. Marshall Institute, a tobacco industry consultant and a prominent skeptic on the issue of global warming] as their top guy to basically say, in the immortal words of the tobacco industry P.R. memo in 1970, "doubt is our product". Not to prove, the point has not been, and is not today, to prove that climate science is wrong. The point is to simply raise enough doubt in the minds of journalists, politicians, the business class, and the general public. To raise enough doubt so that you can blunt the urge and the calls for political reform.
Climate Change 1: Global Warming Food-for-Thought
- Problems with binary (this-or-that) thinking:
- In the 1960s, everyone in popular culture seemed to be discussing B. F. Skinner's question "is it nature or nurture?". Today we know the correct answer is "it is nature and nurture".
- With regard to climate change, most people are repeating the previous mistake by posing the question "is it natural or anthropogenic?" but we already know the answer is "it is natural and anthropogenic".
- More than twelve thousand years ago as the previous glacial period was ending and the Holocene
inter-glacial was beginning, "Canada east of the Rockies" as well as "the North-Eastern United States" were still under the Laurentide
Ice Sheet. Since that time, this 2-3 km (1-2 mile) high ice sheet has retreated to the intersection of the Arctic Ocean and Baffin Island which is proof
that climate warming is a fact (the current warming is a continuation of the warming that ended the ice age). The primary reason
for ice-ages are Milankovitch cycles which include:
- changes in the shape of Earth's orbit around the sun
- changes in axial inclination (currently tilted to 23.44 degrees and decreasing)
- axial procession (a.k.a. wobble; our north pole will come closest to pointing to our North star, Polaris, in 2100)
- Ten thousand years ago, the estimated size of the human population was 5-6 million (although some publications say 1-10 million). Since then, human population is 1,600 times larger at 8.0 billion (2022) and most scientists attribute the population explosion to increased agriculture enabled by natural global warming. There have always been natural greenhouse gases in Earth's atmosphere (CO2 levels historical oscillate between 180 ppm and 280 ppm) but industrial humans began adding much more beginning with the age of steam starting in the 1700s. We now know that the combination of natural greenhouse gases and anthropogenic greenhouse gases are converting a natural warming trend into an environmental disaster (at least one which will hurt the agricultural productivity necessary to support 8.0 billion humans).
- On average, inter-glacial periods last 15,000 years. If we weren't here making things worse, the current inter-glacial period would end in about 6,000 years. Many scientists have suggested that a human population in excess of 8.0 billion people will ensure that the current inter-glacial will never end.
- So here is what I don't understand: If scientists warned us that an asteroid was hurtling toward the Earth, we would do something about it. With regards to climate warming there is a huge push-back by some people claiming: the science is wrong, there is no consensus, etc. Meanwhile, we are heading to destruction just as surely as if an asteroid was headed our way. We can't change Earth's orbit, but we can control our emissions to compensate for it.
Climate Change 2: It Is All About the Ice (polar as well as glacial)
- "Secondary school" science refresher for global warming skeptics:
- Definition 1: one calorie of energy is required to raise the temperature of one gram of water by one
Celsius degree (1°C).
Definition 2: one BTU (British Thermal Unit) of energy is required to raise the temperature of one pound of water by one Fahrenheit degree (1°F). - However, eighty calories of energy are required to convert one gram of zero degree ice into zero degree water (the text-book value is 79.72 calories or 333.55 joules). This value is known as the specific melting heat of ice and is one reason why a small volume of ice can cool a larger volume of liquid (think about that the next time you are sipping drinks around the pool). In a hand held container, the temperatures do not meet in the middle. Instead, the temperature of the liquid drops toward the temperature of ice until no ice remains. Notice that the addition of eighty calories of energy to 0°C ice has not increased temperature; it has only changed the state from solid to liquid.
- Definition 1: one calorie of energy is required to raise the temperature of one gram of water by one
Celsius degree (1°C).
- Polar ice shelves and glaciers are melting at an unprecedented rate which means that they are currently do a reasonably good job of slowing the rise of Earth's average surface temperature (although the CO2 increase began with the beginning of the industrial revolution, things get far worse after human population quadruples between 1900 and 1999).
- Question: so what happens when the ice is gone?
Answer-1: Instead of every 80 calories of thermal energy converting one gram of ice into water, it will raise the temperature of one gram of water by 80 degrees C. Higher temperatures will kill our oceans, increase the size and number of deserts (via affecting Hadley cells), flood most river deltas with salt-water storm surges, increase storm frequency and (to a lesser extent) intensity. Remembering that many river headwaters originate in mountain glaciers (six major rivers in Indo-China begin in the Tibetan plateau), the reduced river flow will reduce the food supply probably killing up to one billion people. (will subsistence farmers on the equator ever be able to buy food from developed countries?)
Answer-2: Once the ice has melted into water, it will be very difficult (maybe impossible) to restore it to its previous condition. Why? From the liquid state you will require the removal of 80 calories to change the state back to ice. This might never happen again until the next ice age. (There is a high probability of the arctic polar ice cap totally melting because, unlike the Antarctic, there is no underlying continent)
Recent bad news: The Wilkins Ice Shelf is comparable in size to the US state of Texas. Although it had been cracking for years, a Connecticut-sized portion began calving into icebergs in April 2009 (although the news media missed it because they were fixated upon the relatively smaller H1N1 Mexican influenza outbreak as well as minutia from Hollywood)
- Post Script: to make matters worse, melting ice is similar to flipping a switch: ice reflects 80% of incident sunlight back into space while water absorbs
80% of incident sunlight. This means that planet Earth is flipping from "reflecting mode" to "absorption mode" which could be the beginning of a thermal runaway
effect. Additional environmental heat will do many things but here are just three:
- Drive the oxygen out of water thus killing the oceans. (Trout and Salmon prefer cold water because cold water is oxygen rich)
- Cause atmospheric oxygen to bind with minerals. Many deserts are reddish-orange due to the combining of oxygen with minerals (oxidization)
- Shorten winter so that disease bearing pests are not properly terminated each year.
- Many people claim the current warming trend is natural and they are partially correct. Earth's current orbital shape around the Sun is nearly circular
(Eccentricity: 0.016710219) but is more elliptical during ice ages (elliptical eccentricity is one of three Milankovitch cycles). Today, man-made greenhouse gas emissions are amplifying a natural warming cycle (positive feedback) which will push
Earth's climate past the tipping point much sooner.
Orbital Forcing
1) Orbital forcing is the effect on climate of slow changes in the tilt of the Earth's axis and shape of Earth's orbit (see Milankovitch cycles in the next section). These orbital changes modulate the total amount of sunlight reaching the Earth by up to 25% at mid-latitudes (from 400 to 500 W/m-2 at latitudes of 60 degrees). In this context, the term "forcing" signifies a physical process that affects the Earth's climate.
2) This mechanism is believed to be responsible for the timing of the ice age cycles. A strict application of the Milankovitch theory does not allow the prediction of a "sudden" ice age (rapid being anything under a century or two), since the fastest orbital period is about 15,000 years. The timing of past glacial periods coincides very well with the predictions of the Milankovitch theory, and these effects can be calculated into the future.
3) Scientists think Milankovitch cycles enable/disable ice ages but climatic feedback loops are responsible for the actual flip. For example, Milankovitch warming causes the oceans to heat up which triggers the release of dissolved CO2, water vapor, and methane hydrates. These added greenhouse gasses raise atmospheric temperatures even higher which melt polar ice (changing albedo from light to dark) as well as melting of permafrost which releases even more methane.Milankovitch Cycles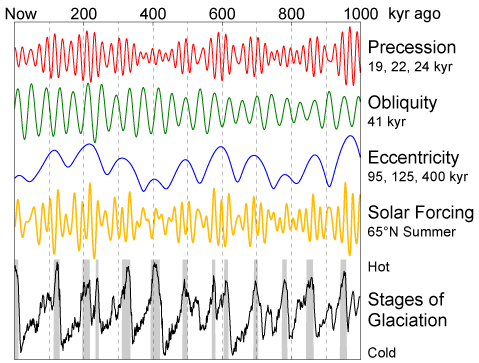
1) Precession is the change in the direction of the Earth's axis of rotation relative to the fixed stars, with a period of roughly 26,000 years. This gyroscopic motion is due to the tidal forces exerted by the sun and the moon on the solid Earth, associated with the fact that the Earth is an oblate spheroid shape and not a perfect sphere. The sun and moon contribute roughly equally to this effect.
2) The angle of the Earth's axial tilt (obliquity) varies with respect to the plane of the Earth's orbit. These variations are roughly periodic, taking approximately 41,000 years to shift between a tilt of 22.1° and 24.5° and back again. When obliquity increases, the temperature difference between winter and summer increases.
3) The shape of Earth's orbit around the Sun is an ellipse and eccentricity being is a measure of the departure from circularity. The shape of the Earth's orbit varies from being nearly circular (low eccentricity of 0.005) to being mildly elliptical (eccentricity of 0.058) and has a mean eccentricity of 0.028. The major component of these variations occurs on a period of 413,000 years. A number of other terms vary between components 95,000 and 125,000 years, and loosely combine into a 100,000-year cycle.
4) The result of these waves combine to enable glaciation cycles with an average period of 100,000 years. (feedbacks from greenhouse gases actually throw the final lever; Volcanoes introduce a randomness which can go either way). Within this cycle you will find an average interglacial period of 15,000 years.
Milankovitch Animations:
Food For Thought: the current warming trend (which started 11,700 years ago at the end of the previous ice age) has enabled the human population to grow to its current size of 6.9 billion. Things got worse with the beginning of the industrial age and the invention of steam engines. The current level of trapped solar energy is too high so humanity must employ geoengineering along with "CO2 reduction" to lower the average temperature so we can maximize agricultural production. Some time in the distant future, humanity will use geoengineering along with "CO2 production" to prevent the temperature from getting too low as we enter the next ice age. Think of both interventions on our part as a cosmic survival test. - So with Milankovitch cycles causing the largest changes, are man-made (anthropogenic) greenhouse gases of little consequence? No.
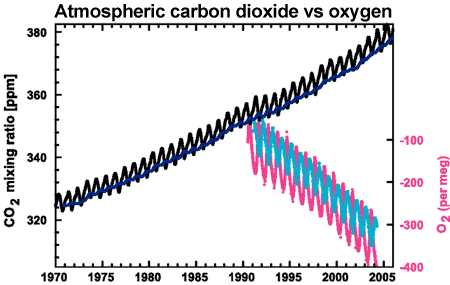
Ice cores from Greenland (Camp Century) and Antarctica (Vostok Station) provide scientists with an atmospheric history going back 400,000 years and 600,000 years respectively. During previous inter-glacial periods, natural warming occurred first which then triggered the oceans to release dissolved CO2 (some sources say there is one molecule of CO2 in the atmosphere for every 50 molecules dissolved in the oceans; the amount released would depend upon the temperature (think warm beer)). With the current inter-glacial, industrial CO2 was released ahead of the warming. When our oceans release dissolved CO2 this time around we will get a double dose. Maybe this is already happening and may be one explanation for the blue spike in the diagram on the right.
p.s. While ice cores trap samples of atmospheric gas, other climate proxies like stalactites, stalagmites, and sediment cores do not. Nevertheless, these three methods do support the theory of Milankovitch cycles as far as temperature and water are concerned. Indian Ocean sediment core "Vema 28-238" is probably the best sample of the lot.
-
To learn more about Milankovitch and climate cycles, read the no-nonsense book "The Discovery of Global Warming" by Spencer Weart. You can purchase a copy or read the whole thing free of charge at the next two links hosted by the American Institute of Physics If you don't want to but the book, you can access it online for free here:
Climate Change 3: Global Dimming (a temporary reprieve?)
Many non-scientists think global warming has stopped but this temporary trend seems to be related to something called "global dimming".Oversimplifying the global warming equation to just two terms:
Resultant environmental temperature = Global warming (via greenhouse gases) - Global dimming (via cloud formation)
With "global dimming", certain kinds of visible pollution (smoke-stack and tail-pipe emissions, volcanoes, etc.) stimulate white-cloud formation which reflects incoming solar energy back into space before it can be converted to trapped heat. This "Global dimming" theory gained unexpected real-world proof when the 9/11 attacks on New York resulted in the grounding of American aircraft for three days. During this time, scientists measured a very noticeable increase in surface temperature.Climate Change 4: A closer look at CO2 (Earth vs. Venus)
caveat-1: what follows are a set of calculations which take numerous liberties in order to do back-of-the-envelope comparisons (the column labelled "solar energy ratio" assumes 100% absorption using an "apparent 2-d area"). But I believe these ball-park results prove my general point.caveat-2: This article had been online for more than 5-years before I learned (2019-10-10) that what I have named "apparent 2-d area" is sometimes referred to by professional scientists as "capture cross section". If doing actual heat capture calculations it might be wise to first multiply "apparent 2-d area" by 0.8 although my intuition tells me the 0.7071 might be a better choice. We can skip this concern when doing comparisons (please redo the my calculations below if you do not believe me)
An optimal CO2 level is required for complex life but too much may be as dangerous as too little
To see what I mean, consider the Wikipedia-sourced data (highlighted in yellow) in the following table:| Object | Temperature (relative comparisons must only be done in Kelvin) |
Distance from Sun km |
Atmospheric Pressure kPa |
Notes | Mean Radius km |
Apparent 2-d Area (million sq-km) |
Albedo (Reflectivity) |
||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Min | Mean | Max | |||||||
| Moon | 100 K |
-46 C 220 K |
390 K |
150 M | ~ 10-7 | Same distance from the Sun as Earth Atmospheric pressure is almost zero Temperature extremes would kill animal life |
1,737 | 9.48 | 0.12 |
| Earth | -89 C 184 K |
15 C 287 K |
57 C 331 K |
150 M | 101 | Same distance from the Sun as our moon Percentage of CO2 is: 0.041 (410 ppm) |
6,371 | 127.52 | 0.30 |
| Venus | 462 C 735 K |
108 M | 9,200 | Hotter than Mercury Percentage of CO2 is: 95 |
6,051 | 115.03 | 0.70 | ||
| Mercury | 100 K |
67 C 340 K |
700 K |
46 M to 70 M |
0 | Cooler than Venus while closer to the sun No atmosphere to speak of |
2,439 | 18.69 | 0.12 |
Initial Observations:
- Comparing Venus to Mercury
- Because an atmosphere can limit radiative loss, Venus (with an atmosphere) is hotter than Mercury (no atmosphere) even though Venus is almost twice as far from the sun as Mercury's average distance.
- Notice the high albedo Venus which should be reflecting 70% of the incoming visible solar radiation.
- Comparing Earth to the Moon (a.k.a. Earth's moon)
- Because Earth's atmosphere limits radiative loss, Earth's mean temperature is 60 Celsius degrees higher relative to our Moon.
- Because the Earth and Moon are the same distance from the sun (on average) we can ignore solar distance and directly compare solar energy and mean
temperatures:
- We start by calculating their apparent two-dimensional area (they appear as flat disks when viewed from the Sun) to determine how much solar energy is intercepted and can see that the Earth is intercepting ~ 13 times more solar energy than the moon.
- But computing the surface area (4 x PI x r2) of both bodies reveals that Earth is ~ 13 times larger so everything cancels out (sort of).
- The Moon rotates only once every 27.3 days so the sun side gets really hot (think of a very slow barbecue) while the dark side gets really cold.
- If the moon rotated as fast as Earth (once a day) then the solar energy would be more evenly distributed across the whole surface.
- If the moon had any real atmosphere it would act as a radiative buffer to "disperse/distribute inbound energy" while "retarding outbound energy loss"
- Lack of atmospheric buffering aside, temperature swings on the Moon are larger because the Moon only rotates once every 27.3 days
We can see CO2 in action (as a warming blanket) by comparing Earth to Venus:
0000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000011111111111111111111111111 -+
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 1 2 3 4 5 -+- million km
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 -+
| | | |
Sun Mercury Venus Earth
50 M-km 108 M-km 150 M-km
- If we were being very simplistic, then we would just compare the solar distances of Venus to Earth (notice that the first three planets are almost at one-third points from the sun). Since the ratio of 108/150 would indicate relative coolness, then an inverse ratio of 150/108 would indicate relative hotness; and that value is 1.39 (Venus should be 1.39 times hotter than Earth).
- However, everyone familiar with radiation knows that simple inverse ratios must be replaced with the inverse-square law. This calculation then becomes (1502 / 1082) = (22,500 / 11,664) = 1.93 (Venus should be 1.93 times hotter than Earth).
- But this comparison is still a bit too simplistic since Venus is ~ 5% smaller than Earth so would intercept a little less solar radiation at the closer position. Here it makes sense to use the radius of the (almost) spherical body to compute the area of an apparent two-dimensional disk as viewed from the sun. Repeating our relative calculations using "squared distances" multiplied by "apparent areas" yields a slightly lower solar collection factor of 1.74 (Venus should be 1.74 times hotter than Earth).
| A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Planet | Mean Temp |
Mean Temp Ratio |
Mean Radius km |
Apparent 2-d Area (for solar collection) M sq-km |
Mean Solar Distance M km |
Solar Distance Squared (F^2) |
Inverse Solar Distance Squared (1/G) |
Relative Solar Collection Factor (E x H) |
Solar Energy Ratio |
Albedo (Reflectivity) |
Albedo Adjust |
Albedo Adjusted Energy Ratio |
| Earth | 287 K | 1.000 | 6,371 | 127.516 | 150 | 22,500 | 4.44e-5 | 0.0056673 | 1.0000 | 0.30 | 0.70 | 1.000 |
| Venus | 735 K | 2.606 | 6,051 | 115.028 | 108 | 11,664 | 8.57e-5 | 0.0098618 | 1.7401 | 0.70 | 0.52 | 0.743 |
- Even though Venus is ~ 5% smaller than Earth, being ~ 28% closer to the Sun results in Venus collecting 1.74 times more solar energy (this calculation ignores albedo)
- If albedo is included then Venus actually absorbs less energy than Earth (0.52 / 0.70 = 0.743). When I first noticed this I assumed a math error on my part but this article shows that my back-of-the-envelope calculations are in the ball park
- Caveats:
- Remember that water boils at 373.1 K (100 C) and most complex forms of life cannot survive 323 K (50 C)
- Earth's maximum surface temperature is already at 53 C which is already 3 C degrees too hot for complex life
- Earth cannot be allowed to warm any further, no matter if the current levels are natural, man-made, or a combination of both.
Additional Solar References:
- https://energyeducation.ca/encyclopedia/Solar_energy_to_the_Earth
- https://ag.tennessee.edu/solar/Pages/What%20Is%20Solar%20Energy/Sun%27s%20Energy.aspx
| Planet | Expected Temperature due to solar capture |
Actual Temperature due to CO2 |
CO2 ppm |
|---|---|---|---|
| Venus | 55 C | 500 C | 960,000 |
| Earth | - 18 C | 15 C | 420 |
| Mars | - 50 C | - 63 C |
Climate Change 5: Global Warming is an observational fact
"Global Warming" is an observational fact. In this controversy, evidence falls into two categories: direct measurements (which started with the invention and distribution of inexpensive, yet accurate, thermometers in the mid 1860s) and proxy measurements.
- Proxy measurements require quite a bit of interpretation (because they cross many scientific disciplines -and- are spotty so do not necessarily represent world wide events) and so should only be left to the experts in the court of peer reviewed science.
- Direct measurements require very little interpretation provided you understand a very small amount of science.
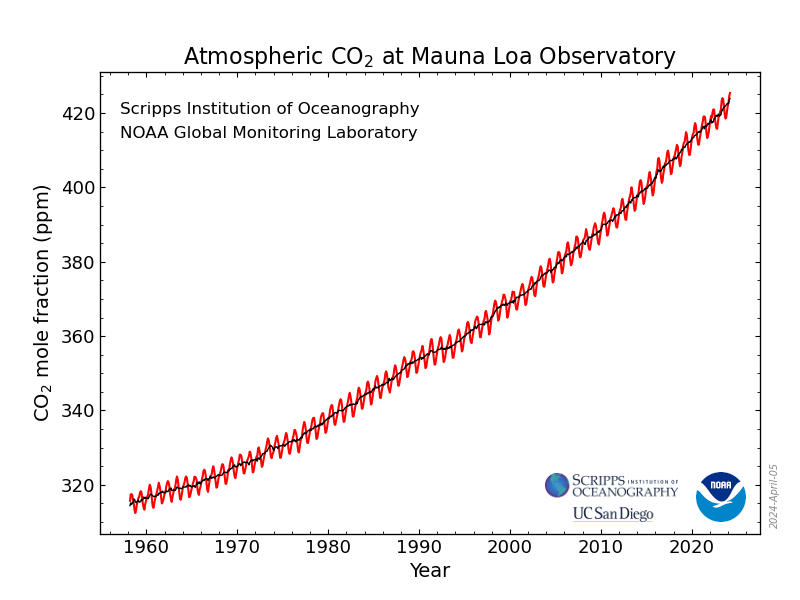
So here are observational facts from reputable science organizations (updated: 2025):
- Average global temperatures have risen 1.50 C (2.7 F) degrees since measurements began in 1880
Direct Measurement: http://climate.nasa.gov and https://www.giss.nasa.gov/research/ - CO2 levels have risen 37% since annual measurements began in 1958
Direct Measurement: https://gml.noaa.gov/webdata/ccgg/trends/co2_data_mlo.png (most recent CO2 data)
Computed Rate of Increase: ((431-315) / (2025-1958)) = (116 / 67) = 1.73 ppm per year - Oxygen levels have fallen (695-103) = 592 per meg since annual measurements began in 1990
Direct Measurement: http://scrippso2.ucsd.edu/ (data sets are freely available for download )
- http://scrippso2.ucsd.edu/faq
quote: These units refer to different types of quantities, so the question needs to be sharpened before it can be clearly answered. Suppose a tree consumes exactly one molecule of CO2 for each O2 molecule produced by photosynthesis. The changes in atmospheric O2 and CO2 near the tree will then be inversely proportional. What is the proportionality factor in per meg/ppm? The answer is 1/.2095 = 4.8 per meg/ppm, where 0.2095 is the O2 mole fraction of air. This can be derived realizing that, because N2 is constant, the relative change in the O2/N2 ratio is the same as the relative change in O2 and calculating the relative change requires dividing by its abundance. - http://ossfoundation.us/projects/environment/global-warming/the-keeling-curves ("O2 Curve" vs. "CO2 Curve")
- https://cdiac.ess-dive.lbl.gov/trends/oxygen/modern_records.html
quote: Oxygen concentrations are currently declining at roughly 19 per meg per year, or about 4 ppm per year. One "per meg" indicates one molecule out of 1,000,000 oxygen molecules, or roughly one molecule in 4.8 million molecules of air. - https://skepticalscience.com/human-fingerprint-in-global-warming.html
- http://scrippso2.ucsd.edu/faq

- Sea-levels are rising -AND- the rate-of-rise is has more than doubled
- Nineteenth century: average sea level rise was measured to be: 1.4 mm per year
- much of this data comes from military sources like the British Navy
- calculation: 1.4 mm * 100 = 14 cm (5.5 in) per century
- Twentieth century: average sea level rise was measured to be: 1.7 mm per year
- calculation: 1.7 mm * 100 = 17 cm (6.7 in) per century
- Precision RADAR data from orbital satellites shows the new rate in 2022 to be 3.9 mm per year
- calculation: 3.9 mm * 100 = 39 cm (15.3 in) per century
- https://earthobservatory.nasa.gov/images/150192/tracking-30-years-of-sea-level-rise
- it now appears that the collective activity of 4-5-6-7-8 billion people over the past 50-years is responsible for this rate increase
- The 2022 population of Earth now exceeds 8.0 billion (humanity adds another billion every 12 years)
- Precision RADAR data from orbital satellites shows the new rate in 2025 to be 4.62 mm per year
Direct Measurements:- https://climate.nasa.gov/vital-signs/sea-level/ <<<--- click here for an up-to-date graph
- http://sealevel.colorado.edu/
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sea_level_rise (4.62 mm per year in 2025)
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Scientific_concensus_on_climate_change
- melting glaciers as well as polar ice which directly contributes directly to level rise
- warmer water occupying a slightly larger volume (the rise will continue after all the ice is melted)
- Humanity is still coming out of the ice-age that ended 11,700 years ago so some of this warming/melting is natural. However, unlike the past half-dozen ice-ages, this one happened at a time that human numbers exceeded 1 billion people coincident with a "CO2 liberating" industrial age. The human population of Earth now exceeds 8.0 billion
- Nineteenth century: average sea level rise was measured to be: 1.4 mm per year
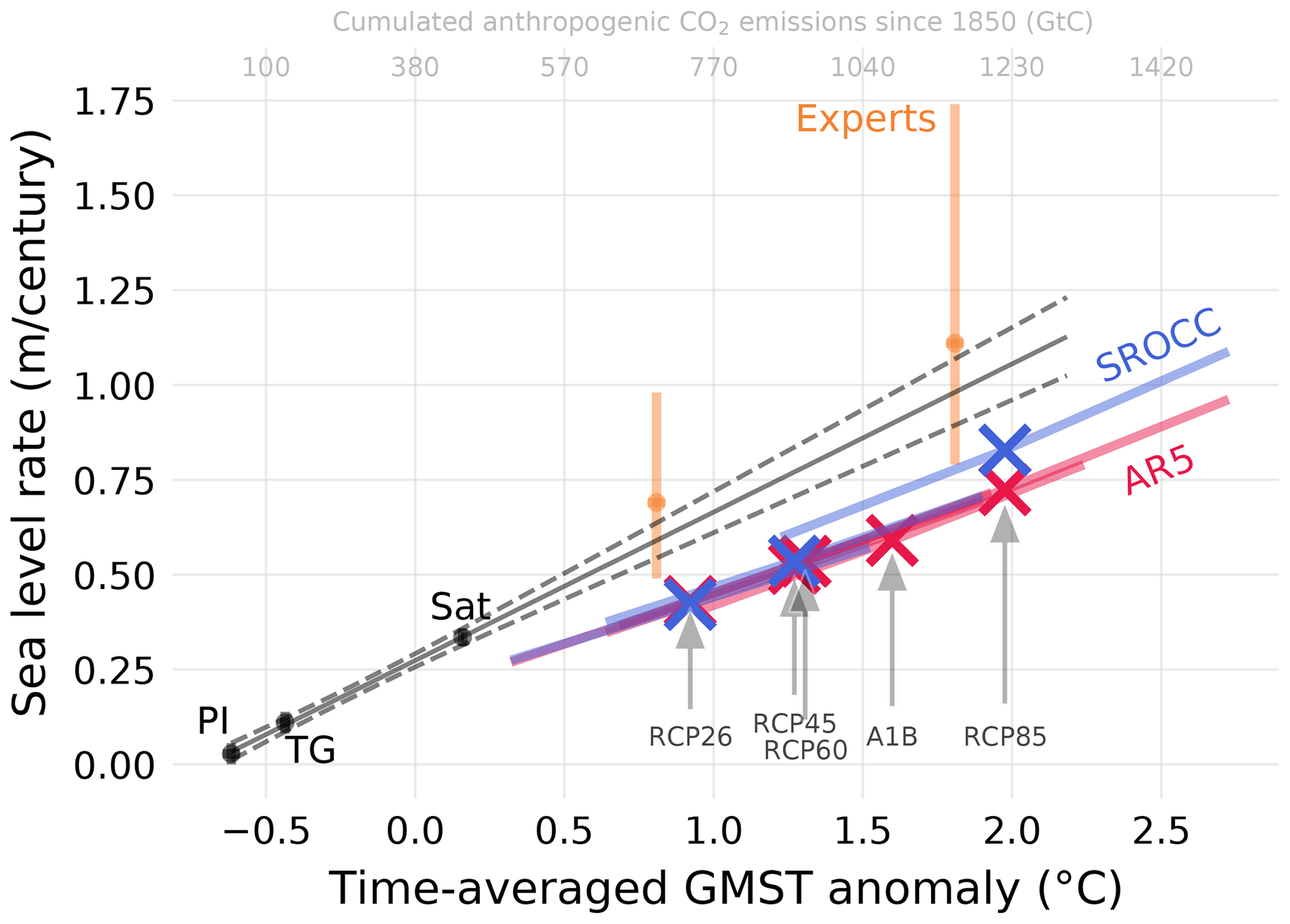
- Future bad news?
4.62 mm per year is a 'global average'. Multiplying by 100 yields 462 mm (18.4 inches) per century if the annual rate-of-rise fell to zero.
From this article we read: "The sea level will not rise uniformly everywhere on Earth, and it will even drop slightly in some locations, such as the Arctic. Local factors include tectonic effects and subsidence of the land, tides, currents and storms".
additionally: The contents of this scientific paper from Denmark ( https://os.copernicus.org/articles/17/181/2021/ ) are more troubling. The first line of the abstract reads: "Recent assessments from the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) imply that global mean sea level is unlikely to rise more than about 1.1 meters within this century but will increase further beyond 2100". This statement infers that a rise of one meter (39 inches) by the end of this century is within the scope of possibility.
From this IPCC 2021 summary we read this very troubling line: Sea-level rise by 2100 is likely to be from half to one meter, but two to five meters is not ruled out, as ice sheet instability processes are still poorly understood. - The burning of fossil fuels is mostly to blame because there is too little Carbon-14 (or Carbon-13) found in
atmospheric CO2
Facts:- If current CO2 levels were produced by volcanoes, then there would be a whole lot more of the isotope known as carbon-13 (13C) found in our current atmosphere.
- If current CO2 levels were produced by the living biosphere, then there would be a whole lot more of the isotope known as carbon-14 (14C)
found in our current atmosphere. It is not found in multiple million-year-old petroleum because the half-life
of carbon-14 is 5,730 years which means that it has all changed into nitrogen-14 due to beta decay.
Links:
Climate Change 6 - Incontrovertible Facts
- Proof of Climate Change (without conspiracy theories about "urban island heat effects", or "UAH datasets", or "Climategate Emails") More
than 200 years ago at the beginning of the Industrial Revolution, scientific explorers like Alexander
Humboldt and Aimé Bonpland (to only name two of many) made detailed observations of flora and fauna
throughout the world. It was Humboldt who first noticed biological similarities between "increases in latitude" and "increases in elevation" which now goes by the
name Elevational Diversity Gradient.
Description: As you move up the side of any sufficiently high mountain you will encounter biological changes previously thought possible only by moving closer to either planetary pole. You will first encounter tree lines, then shrubs, then mosses and lichens, then snow lines.
So it should be no surprise that all these lines in all locations have moved higher in the past 200 years. Here is one recent publication of many:
Up-slope migration of tropical plants due to climate change
http://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2015/09/150914215603.htm - quote: The plants on the highest mountain in Ecuador have migrated more than 500 meters (1640 feet) higher during the last two centuries. This is determined in a new study, in which researchers compared Humboldt's data from 1802 with current conditions.
Comments:- So you don't trust the observations of a dozen similarly minded scientific explorers from 200 years ago? It seems that drawings, paintings, then finally photography (decades later) by tens of thousands of observers around the world recorded similar lines. All you need to do is to compare what was recorded back then with what you see now
- Visit this location further down this page to see additional long term observations
- While the Industrial Revolution brought countless benefits to humanity, it was powered by fossil fuels which released CO2. This was not a problem as long as humanity was planting as many trees as they burned (the original definition of "green energy"). But coal and oil are forms of "carbon-based bio-accumulated solar energy" collected over tens of millions of years but released in just the last 250.
Climate Change 7 - Improving atmospheric CO2 extraction of trees
(a temporary solution which is better than nothing)
First, a few basic facts about photosynthesis
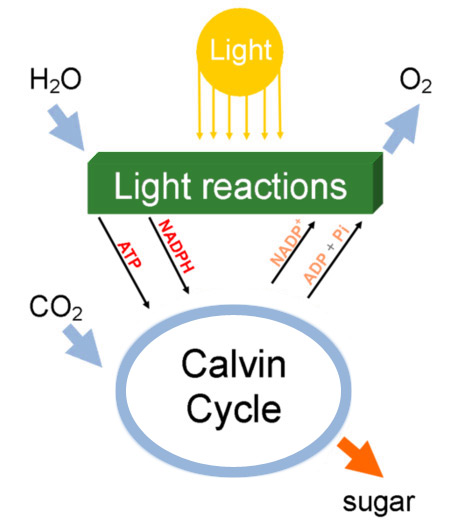
Chemical formula for photosynthesis
- A primary grade-school explanation of photosynthesis tells the young student that "CO2 is converted into O2".
Sometimes a very simplified chemical formula is provided like this one:
CO2 + H20 + energy = (CH2O) + O2 - Secondary-school biology classes introduce more details including a properly balanced chemical formula similar to this one:
6CO2 + 6H2O + photons = C6H12O6 + 6O2 - College courses in molecular biology fill in the missing intermediate steps which show that O2 is only liberated by the photolysis of water (the original research was done by scientists using radioactive tagging). So it is more accurate to say "H2O is split by photolysis into O2 and H with the O2 immediately discarded to the atmosphere. Later in the process, H is combined with atmospheric CO2 to produce glucose"
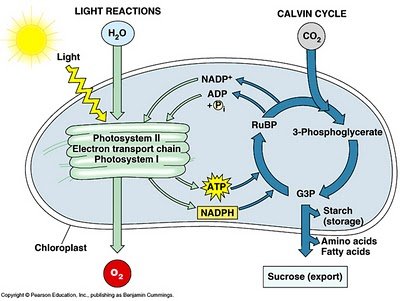
- The left-hand side of the diagram was previously known as The Light Reactions but most publications this side of Y2K refer to it as Light-dependent
Reactions
- Light induces photolysis (splitting of water into hydrogen and oxygen) which liberates an electron along with a small amount of energy to power other chemical
reactions (see: electron transport chain for details)
- one liberated electron is used to bind phosphorous (+P) with ADP yielding ATP (the power transfer molecule of most biological systems including humans)
- energy is used to bind atomic hydrogen (H) to NADP+ yielding NADPH (to transport hydrogen to the other side of the diagram)
- some energy is used to bind atomic oxygen (O) into molecular oxygen (O2) which is released to the atmosphere
- observation: You might wonder why Photosystem II is before Photosystem I. These labels relate to
the order in which they were discovered and were not changed because this would conflict with previously published literature.
- Light induces photolysis (splitting of water into hydrogen and oxygen) which liberates an electron along with a small amount of energy to power other chemical
reactions (see: electron transport chain for details)
- The right-hand side of the diagram was previously known as The Dark Reactions but most publications this side of Y2K refer to it as Light-independent
Reactions
- hydrogen (from NADPH) is combined with atmospheric CO2 to produce glucose
- the whole thing is powered by converting ATP back into ADP (which frees a +P to be used in the next turn if the cycle)
So we now know that sunlight (input 1) and H20 (input 2) are more important than CO2 (input 3) because the photolysis of water in Photosystem II (on the left-hand side of the diagram) powers the Calvin Cycle (on the right-hand side of this diagram). We already know that too much sunlight, or too much water, will kill a plant so pushing in additional carbon-dioxide makes little sense (but each ingredient is considered a limiting factor to maximum productivity). But because increasing atmospheric CO2 is driving up atmospheric temperatures, we can expect increased evaporation. This will result in less bio-available water to plants.
Suggestions to maximize CO2 removal
- the above notes show that a lack of water is just as critical as a lack of sunlight
- so if the ground is not frozen, and sunlight is sufficient, each tree will require water each day.
- if you suspect the roots are not supplying sufficient water then I suggest you begin with applying a minimum of 1 Liter (1 Quart) of water each day to each tree
- caveat: over watering can, potentially, wash away nutrients; under watering on a sunny day could cause leaves to dry out and/or burn
- You could water manually or resort to tree watering bags
Planting trees is just a Band-Aid solution
While I am a huge proponent of planting trees, and watering them properly to improve CO2 draw-down, this is a very temporary measure. I should not need to point out that trees can only sequester CO2 while they are in sunlight, in non-frozen soil, and are alive. As soon as a tree dies, microbes will break it down causing a massive release of carbon in the forms of CO2, methane, and other related gases. This means that a tree is just a stop-gap measure -AND- dead trees need to be replanted immediately. Also, it should be obvious to all that a newly planted young tree will not have the same CO2 draw-down capacity of a large mature tree.The industrial revolution(s) caused this problem and I fear that an industrial revolution can only fix it with Direct Air Capture technology from companies like this one: ...but I also fear that the current fossil fuel industry will think that technology like this will allow them to continue to pollute.
Details about burning Gasoline ('petrol' for you Brits)
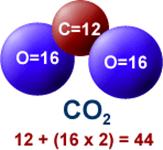
will produce 18 pounds (8.16 Kg) of carbon dioxide (CO2)
Why? While the "Carbon" in CO2 does come from the fuel, the Oxygen comes from the atmosphere which is usually never considered by the non-specialist.
DETAILS: When gasoline burns, the Carbon and Hydrogen separate (which releases energy in the form of heat). The Hydrogen combines with Oxygen (from the atmosphere) to form water vapor (H2O) while the Carbon combines with Oxygen (from the atmosphere) to form carbon dioxide (CO2). A carbon atom has an atomic weight of 12, and each oxygen atom has an atomic weight of 16, giving each single molecule of CO2 an atomic weight of 44 (12 + 2 x 16 ).
COMMENT: It now appears that that Carbon Capture and Storage (CSS) technology will never be practical since the required amount of energy to compress-store this volume of gas would be too large.
The players in this drama
| Substance | Chemical Formula | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Molecular Oxygen | O2 | |
| Octane (gasoline or petrol) | C8H18 | |
| Carbon Dioxide | CO2 | |
| Water | H2O | |
| Molecular Nitrogen | N2 | An inert gas at room temperature. Can bond with O to produce yellow smog |
Atomic Masses from the Periodic Table
| Element | Atomic Number | Atomic Mass |
|---|---|---|
| Hydrogen | 1 | 1 |
| Carbon | 6 | 12 |
| Oxygen | 8 | 16 |
Calculations:
- (balanced) Burn Equation: 2 C8H18 + 25 O2 → 16 CO2 + 18 H2O (reference)
- Gasoline Mass Calculation
- Total octane mass (from the left-hand side of the equation):
- 2 x ((C x 8) + (H x 18))
- 2 x ((12 x 8) + (1 x 18))
- 2 x (96 + 18)
- 2 x 114 = 228
- Total Oxygen Mass (from the left-hand side of the equation):
- 25 x (O x 2)
- 25 x (16 x 2)
- 25 x 32 = 800
- Total octane mass (from the left-hand side of the equation):
- Carbon Dioxide Mass Calculation
- Total Carbon Dioxide mass (from the right-hand side equation):
- 16 x ((C x 1) + (O x 2))
- 16 x ((12 x 1) + (16 x 2))
- 16 x (12 + 32)
- 16 x 44 = 704
- Ratio: 704 / 228 = 3.09 (therefore the resultant CO2 is ~ 3 times heavier than gasoline just consumed)
- Total Carbon Dioxide mass (from the right-hand side equation):
- Water Vapor Mass Calculation
- Total Water Vapor mass (from the right-hand side equation):
- 18 x ((H x 2) + (O x 1))
- 18 x ((1 x 2) + (16 x 1))
- 18 x (2 + 16)
- 18 x 18 = 324
- 18 x ((H x 2) + (O x 1))
- Ratio: 324 / 228 = 1.42 (therefore the resultant water vapor is ~ 1.4 times heavier than gasoline)
- Total Water Vapor mass (from the right-hand side equation):
Is 'too much' CO2 good or bad?
The guy in the office next to me is convinced that 425 ppm of CO2 (click
here for the current number) is a tiny fraction of gas and is of no concern to life on Earth. Well, almost anyone with a basic knowledge of biology already
knows that placing a plastic bag over your head will quickly cause problems (headaches) due to a slightly elevated CO2 level, long before the O2
level drops causing unconsciousness. This is the main reason why CO2 scrubbers
are required technology on aircraft and submarines. Simply adding additional O2 is not enough, you must remove the CO2
Getting back to tiny numbers for a moment, doing the math shows that 425 ppm of CO2 is equivalent to an atmospheric concentration of 0.0425
percent. This doesn't sound like much until you recall that a blood alcohol level of anywhere
between 0.05 and 0.08 percent (depending upon local laws) means that society considers you legally intoxicated. Point Zero Five is the colloquial
phrase for 0.0500 percent which is only a tiny bit higher that 0.0425 percent.
| calculation | result-1 | result-2 | calculation description | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PPM | 425 / 1,000,000 | 4.25e-4 | 0.000425 | 425 ppm expressed as a decimal |
| Percent | 0.000425 * 100 | 0.0425 % | 425 ppm expressed as a percent |
I must point out that "atmospheric CO2 concentrations" and "blood alcohol ratios" do not have the same effect on the human body. Publications by the U.S. Navy indicate that atmospheric CO2 levels of 0.5% will induce physiological changes such as nausea and headaches. This ad-hoc comparison seems to indicate that humans tolerate CO2 approximately ten times better than alcohol (0.50 / 0.05 = 10). Nevertheless, you cannot dismiss numbers just because you consider them small. For example, compounds like the recreational drug LSD have their effect in parts per billion (denominator has nine zeros) while dioxins like agent-orange are dangerous in parts per trillion (denominator has twelve zeros).
Reaping What We Sow :: WE ARE undoubtedly pumping ever more carbon dioxide into the air. But did you know that this also silently adds unwanted carbs to bread, cereals and salad and cuts vital protein and mineral content? This nutritional blow is now worrying the world's most powerful nation. For the first time it forms a key finding in an official report on the health impacts of climate change in the US, drawn up by the Global Change Research Program (USGCRP) and unveiled by the White House this week. Why would more CO2 mean poorer food? Photosynthetic organisms, such as plants, are the carbohydrate factories of the world. They convert CO2 and water into gigatons of starch and sugars every year. And every year since the industrial age began, we have steadily fed them more CO2. Plants respond by building more carbohydrates but less protein into tissues. This means a higher ratio of carbs to protein in plants, including key crops such as wheat, rice and potato. This is a double whammy: protein deficiency afflicts the developing world, while excess carbohydrate consumption is a worry in the obesity-riven developed world. This is not the only nutritional impact. To capture CO2, plants open pores in their leaves. These stomata let in CO2 but allow water out: plants compensate by sucking moisture from the soil. Transpiration, as this process is called, is a major hydrological force. It moves minerals essential for life closer to the roots, nourishing plants and ultimately us. But plants respond to high CO2 by partially closing stomata and losing less water. This reduces the flow of nutrients to roots and into plants. Less minerals but more carbs creates a higher carbs-to-minerals ratio in crops and food. In an elevated CO2 world, every serving of bread, pasta, fruits and vegetables delivers more starch and sugar but less calcium, magnesium, potassium, zinc, protein and other vital nutrients. Over a lifetime, this change can contribute to weight gain. Hidden hunger, the result of diets rich in calories but poor in vital nutrients, was mainly a developing world problem. But in 2002, New Scientist predicted that "elevated CO2 levels threaten to bring the problem to Europe and North America". Skepticism made it difficult to secure funding for testing this prediction and slowed progress by a decade. However, the conclusion is now unequivocal: rising CO2 depletes protein and minerals in most food that underpins human nutrition across the world. Skeptics {alt: Sceptics} like to claim that rising CO2 is a boon because it boosts crop yields. But as US Department of Agriculture scientist Lewis Ziska put it "elevated CO2 could be junk food" for some plant species. There really is no such thing as a free lunch with climate change. --
Cognitive Dissonance (or, "How We Fool Ourselves")
An alternative explanation for the bizarre claims of "science deniers" involves a "creative injection" solution to the problem of "Cognitive
Dissonance". What is "CD"? Briefly, it is the sensation of a "potential difference" between conflicting ideas which, under normal circumstances, compels you to
change your behavior.
Consider this example:
- you want to live a long healthy life
- you enjoy smoking tobacco
- you have been told smoking is bad for your health
- these facts cause an internal thought-conflict (dissonance) in your brain. To minimize this dissonance:
- most people will stop smoking (the pleasure of smoking is replaced with the pleasure associated with removed dissonance)
- but a smaller group of people will find it easier to inject one, or more, creative counter-balancing thoughts like "the science is wrong", "the science is not
100% certain", "scientists are part of a global conspiracy theory to confuse the public while reducing my personal freedoms", etc.
(by the way, although the science may not be 100% correct, it is often "correct enough" to make a good decision)
Citizens who have spent large amounts of money on Hummers, SUVs or "multiple family vehicles" will create a dissonance if they "accept climate change" so will find
it easier to pick from a cornucopia of creative alternatives like: "the Earth's climate is not changing", "The Earth's climate has warmed before", "7 billion humans
can not change Earth's climate", "the science is uncertain", "god will intervene before things get too bad", etc. Introducing other unknowns like a carbon-tax only
increases dissonance. But in the end they are just like the people who think they can continue smoking with no consequences.
Literary (fictional) Observation: two technicians discuss "the conflict of positronic potentials" in chapter 2 of the book "I,
Robot". Since this story was written in the 1940's, is it possible it was the germ idea for Cognitive Dissonance which first appears in the
literature in 1956?
A possible reinforcing effect to Cognitive Dissonance is something known as the Dunning-Kruger effect after the publication of their 1999 paper titled: "Unskilled and Unaware of It: How Difficulties in Recognizing One's Own Incompetence Lead to Inflated Self-Assessments"
- video 1: https://www.youtube.com/watch?feature=player_detailpage&v=ZtQSv60fbrE (4 min, 56 sec)
- video 2: https://www.youtube.com/watch?feature=player_embedded&v=VFFczMYJoSY (7 min, 10 sec)
- article: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Dunning-Kruger_effect
Politics and Anti-Science
Food-for-thought publications on the current mess:
- The Republican War on Science
- Unscientific America
- How does the anti-science view get traction?
Excerpt from: Deja vu All Over Again
This is how it begins: Proponents of a fringe or non-mainstream scientific viewpoint seek added credibility. They're sick of being taunted for having few (if any) peer reviewed publications in their favor. Fed up, they decide to do something about it.
These "skeptics" find what they consider to be a weak point in the mainstream theory and critique it. Not by conducting original research; they simply review previous work. Then they find a little-known, not particularly influential journal where an editor sympathetic to their viewpoint hangs his hat.
They get their paper through the peer review process and into print. They publicize the hell out of it. Activists get excited by the study, which has considerable political implications.
Before long, mainstream scientists catch on to what's happening. They shake their heads. Some slam the article and the journal that published it, questioning the review process and the editor's ideological leanings. In published critiques, they tear the paper to scientific shreds.
Embarrassed, the journal's publisher backs away from the work. But it's too late for that. The press has gotten involved, and though the work in question has been discredited in the world of science, partisans who favor its conclusions for ideological reasons will champion it for years to come.
The scientific waters are muddied. The damage is done. (read more...)
Art Imitates Life?
Quotes from the 1973 movie "Soylent Green"- The Year: 2022. The Place: New York City. The Population: 40,000,000
- Governor Santini is brought to you today by Soylent Red, and Soylent Yellow. And, new, delicious, Soylent Green: The "miracle food" of high energy plankton, gathered from the oceans of the world. Due to its enormous popularity, Soylent Green is in short supply, so remember—Tuesday is Soylent Green day.
- You know, when I was a kid, food was food! Until our scientists polluted the soil... decimated plant and animal life. Why, you could buy meat anywhere. Eggs, they had. Real butter. Fresh lettuce in the stores! How can anything survive in a climate like this? A heat wave all year long! The greenhouse effect! Everything is burning up!
- You don't understand… I've seen it. I've seen it happening. The ocean is dying, the plankton is dying… It's people! Soylent Green is made out of people. They're making our food out of people. Soon, they'll be breeding us like cattle—for food! You gotta tell 'em! Listen to me, Hatcher! You gotta tell 'em—SOYLENT GREEN IS PEOPLE! We gotta stop them! Somehow! Listen! Listen to me… PLEASE!!!
Climategate Information from 2009 (preserved but not deleted)
content moved here to reduce the size of this page
Links
- https://skepticalscience.com/ (just the facts)
- https://www.youtube.com/user/potholer54 (great debunker of internet-generated nonsense)
- Global Warming: An Inconvenient History
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=GGtAilkWTtI - Science of Doom
- Introduction to heat pumps
- Introduction to climate modeling
- https://www.wondrium.com/earth-s-changing-climate
- Humanity's coming Dark Age
 Back to Home
Back to HomeNeil Rieck
Waterloo, Ontario, Canada.